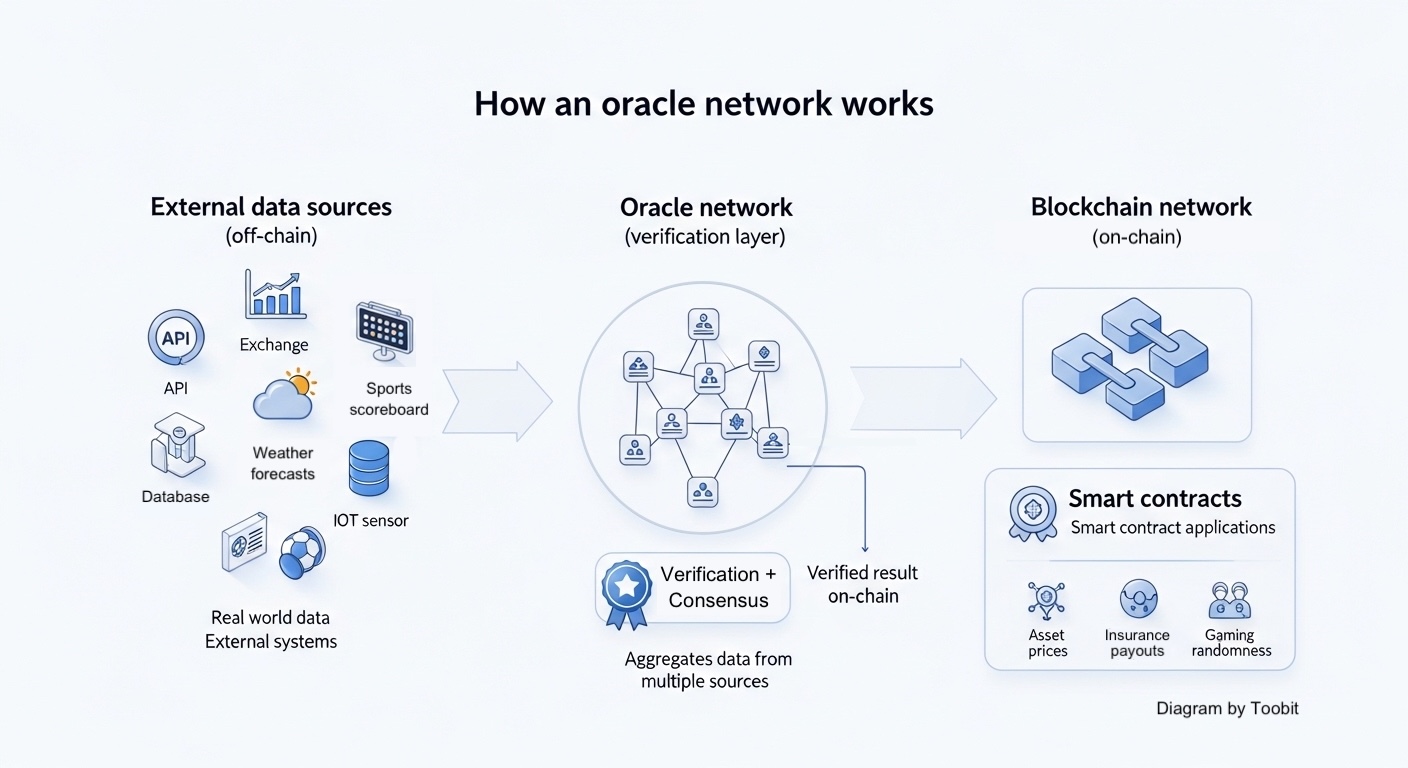
What is an oracle network?
A blockchain network is excellent at recording blockchain transactions, enforcing rules, and keeping everyone in sync. But it has a built-in limitation: Public blockchains cannot natively read external data from the internet, Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), databases, or other external systems.
That gap is exactly what a blockchain oracle, or oracle network, solves.
An oracle network is infrastructure that lets smart contracts use real world data.
It works by pulling external data from multiple sources (APIs, exchanges, databases, or other external systems), then having independent nodes verify and aggregate data before publishing a final result on-chain. That way, a smart contract can rely on trusted data without depending on a single source.
Diagram showing how an oracle network usually works. Source: Toobit.
Why do we need oracle networks?
Blockchains stay secure by requiring agreement. Every node must reach the same state using the same inputs.
If smart contracts could freely pull data from the internet, different nodes could see different results at different times. That breaks verification and can break consensus.
This is known as the oracle problem: Smart contracts cannot securely and reliably access real-world data on their own.
Oracle networks solve this by creating a structured path for off-chain data and compute to become verifiable on-chain inputs.
How do oracle networks work?
In short, oracle networks provide immediate, accurate price feeds for assets, essential for decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. Most oracle networks follow a simple flow that looks similar to the below:
-
A smart contract requests data
A DeFi protocol or other smart contract application needs something like asset prices, proof that an event happened, or a compliance signal. -
Nodes fetch data from multiple sources
Decentralized oracles protect Total Value Locked (TVL) in DeFi from manipulation by using multiple verified nodes.
Independent nodes fetch data from APIs, data vendors, sensors, or other external systems. Using multiple sources improves reliability and reduces single-source risk. -
They verify and aggregate data
The network aggregates data from multiple data sources, often using a median or similar method, to filter outliers and improve reliability. -
The result is posted on-chain
That verified value becomes available to smart contracts as an input for executing logic and settling contractual agreements.
Security is the point. Decentralized oracles aim to make dishonest reporting expensive and easy to detect through monitoring, reputation, staking, and transparent performance.
What kinds of data can an oracle deliver?
Oracle networks are not just "price feeds." They can support several categories of trusted external information.
Data oracles
These deliver prices, rates, indices, and other market data used by DeFi protocols and exchanges.
Common real-life use cases:
-
Lending and borrowing: Collateral values and liquidation thresholds
-
Derivatives: Pricing, funding logic, and settlement
-
Stablecoins: Monitoring collateral and reserve-related signals
Cross-chain interoperability (CCIP)
Some oracle systems help connect blockchain networks by verifying that something happened on one chain before triggering logic on another chain. This supports CCIP, like messaging and moving digital assets between networks.
Additionally, oracle networks can help facilitate regulatory compliance by integrating identity data for compliance checks during on-chain settlement.
Verifiable randomness
Blockchains are deterministic, meaning "random" is tricky.
Verifiable randomness gives provably fair random outputs for real-life use cases like gaming, non-fungible token (NFT) trait assignment, raffles, and event-based mechanics.
Verifiable compute
Some workloads are too expensive to run on-chain. Verifiable compute lets an oracle perform heavy compute off-chain, then return results with proofs a smart contract can verify.
This can support analytics, optimization, and certain AI workflows while reducing on-chain costs and keeping verification on-chain.
Popular oracle networks right now
Here are concrete examples of oracle networks that are widely used today, plus real use cases you can point to.
-
Chainlink
What Chainlink is known for
Price feeds, verifiable randomness, and CCIP tooling.
Where Chainlink is used
Aave reported that it uses Chainlink Price Feeds in production markets to source decentralized price data from multiple sources.
Real use case of Chainlink
Chainlink's own docs cite perpetuals platforms such as GMX relying on feeds to validate off-chain data so deposits and withdrawals execute at correct market value.
Why is Chainlink ranked as "popular"
DefiLlama's oracle dashboard shows Chainlink leading by Total Value Secured (TVS), which is a practical proxy for how much value depends on its oracle outputs.
How to start trading Chainlink (LINK)
Chainlink powers real-world data for the entire industry. If you're ready to trade the backbone of modern smart contracts, Toobit makes it smooth from start to finish.
-
Pyth Network
What Pyth Network is known for
High-frequency market data delivery and pull or push designs depending on chain and integration.
Where Pyth Network is used
Pyth's own blog describes its push oracle as widely adopted on Solana and ties that adoption to "value secured" metrics on the network.
-
RedStone
What RedStone is known for
Modular, on-demand data delivery approaches that aim to reduce always-on posting costs.
Where RedStone is used
Documentation from TON describes integrating RedStone as a pull oracle design for bringing real-time data into contracts when needed.
Why is RedStone ranked as "popular"
DefiLlama lists RedStone with multi-billion TVS, with protocol rankings showing where that dependency comes from.
-
API3
What API3 is known for
"First-party" oracle design, aiming to connect APIs directly to smart contracts with fewer intermediaries.
Where API3 is used
Ecosystem docs such as Sei's describe API3 as a decentralized oracle network providing real-time data feeds for smart contracts.
-
Band Protocol
What Band Protocol is known for
Delivering real-world data to smart contracts and multi-chain oriented oracle infrastructure.
-
Tellor
What Tellor is known for
Permissionless, censorship-resistant data reporting and validation.
Note: People often compare oracle popularity using market cap, but "popular" in infrastructure usually shows up more clearly in usage metrics like integrations, incident track record, and how much value depends on the network's outputs (TVS is one lens).
The bottom line
Oracle networks solve a simple but critical issue, where smart contracts cannot access external data safely on their own.
By pulling from multiple sources, verifying outputs, and publishing trusted results on-chain, oracle networks let decentralized applications (dApps) execute real logic tied to real-world data.
That is how blockchains move from isolated ledgers to systems that can price assets, run protocols, trigger insurance, power games, and connect networks.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, legal, or investment advice.
How to buy crypto on Toobit
To buy crypto on Toobit, create an account, complete verification, and go to Buy Crypto. Choose a token, select a payment method, and confirm the purchase. Your assets will appear in Spot Account once the transaction settles.
Congratulations, you now know how to purchase crypto on Toobit!